Top 10 Cybersecurity Trends Every U.S. Business Needs to Know in 2025
Top 10 Cybersecurity Trends Every U.S. Business Needs to Know in 2025 are reshaping the digital landscape, requiring organizations to adapt swiftly to protect their assets and data. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, businesses must stay ahead of potential vulnerabilities. The first trend is the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) in both offensive and defensive cybersecurity strategies. AI-powered tools can detect anomalies and respond to threats in real-time, but they also pose risks when exploited by malicious actors. 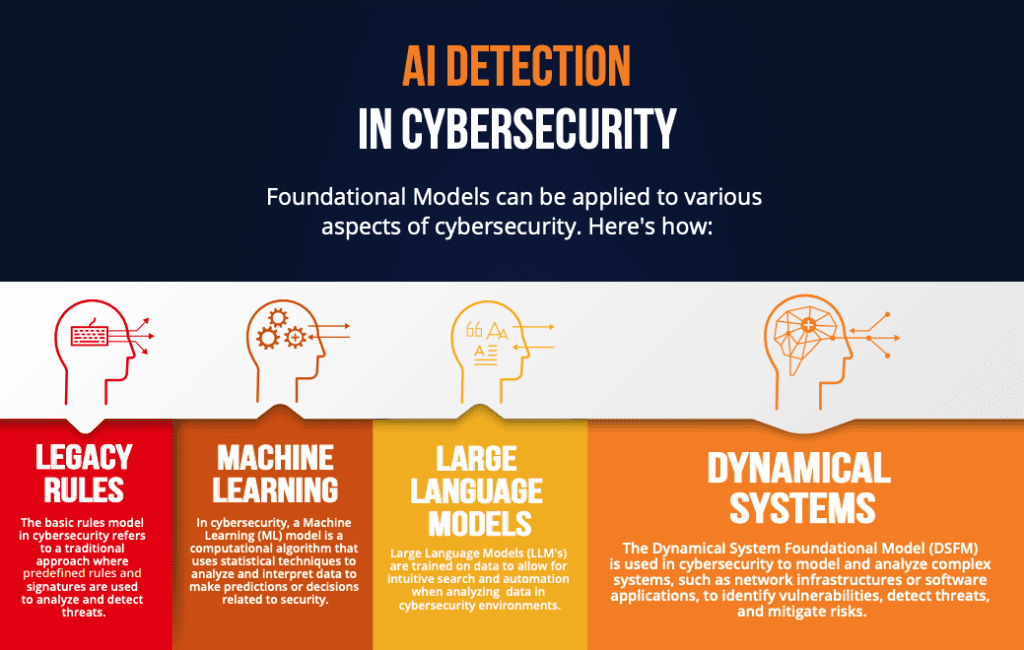 Businesses must invest in AI-driven solutions while ensuring they have robust protocols to prevent misuse.
Businesses must invest in AI-driven solutions while ensuring they have robust protocols to prevent misuse.
Another critical trend is the expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) in corporate environments. With more devices connected to networks, the attack surface grows significantly. From smart thermostats to industrial sensors, each device represents a potential entry point for hackers. Companies need to implement strict IoT security policies, including regular firmware updates and network segmentation to isolate vulnerable devices.
Cloud security remains a top priority as more organizations migrate to cloud-based infrastructures. While cloud providers offer advanced security measures, businesses must take responsibility for securing their own data. This includes adopting multi-factor authentication, encrypting sensitive information, and conducting regular audits to identify and address vulnerabilities. The shift to hybrid and multi-cloud environments adds complexity, requiring businesses to maintain consistent security practices across all platforms.
The rise of quantum computing poses a new challenge for cybersecurity. Quantum computers have the potential to break traditional encryption methods, rendering current security protocols obsolete. To prepare for this, businesses should begin exploring post-quantum cryptography solutions that can withstand quantum attacks. Early adoption of these technologies will be crucial in maintaining long-term data integrity.
Supply chain attacks have become increasingly common, targeting third-party vendors and software providers. The SolarWinds breach in 2020 is a prime example of how a single compromised vendor can affect thousands of organizations. Businesses must conduct thorough security assessments of their suppliers and implement strict access controls. Additionally, continuous monitoring of supply chain activities can help detect and mitigate threats before they escalate.
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is gaining traction as a proactive approach to cybersecurity. Unlike traditional models that assume internal networks are secure, ZTA requires verification for every user and device attempting to access resources. This model minimizes the risk of insider threats and reduces the impact of breaches by limiting lateral movement within networks. Implementing ZTA involves deploying identity and access management systems, micro-segmentation, and continuous monitoring.
Ransomware continues to be a major threat, with attackers targeting critical infrastructure and demanding large sums for data decryption. The rise of ransomware-as-a-service has made it easier for less-skilled hackers to launch attacks. Businesses should prioritize regular data backups, employee training on phishing awareness, and incident response planning. Investing in endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions can also help identify and neutralize ransomware threats quickly.
Regulatory compliance is another key factor influencing cybersecurity strategies. Laws such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) impose strict requirements for data protection. Non-compliance can result in significant fines and reputational damage. Businesses must stay informed about evolving regulations and integrate compliance into their overall cybersecurity framework.
Employee education and awareness play a vital role in preventing cyber incidents. Phishing attacks, social engineering, and weak passwords remain common entry points for hackers. Regular training sessions, simulated phishing exercises, and clear security policies can help employees recognize and report suspicious activities. A culture of security awareness can significantly reduce the risk of human error leading to breaches.
Finally, the integration of cybersecurity with business continuity planning is essential for resilience. Organizations must develop comprehensive strategies to recover from cyber incidents without disrupting operations. This includes having backup systems, disaster recovery plans, and communication protocols in place. By aligning cybersecurity with business goals, companies can ensure they are prepared for any eventuality.
As 2025 approaches, U.S. businesses must remain vigilant and proactive in addressing emerging cybersecurity challenges. Staying informed about the latest trends and implementing best practices will be crucial in safeguarding digital assets and maintaining customer trust. By embracing innovation while prioritizing security, organizations can navigate the evolving threat landscape with confidence.
Comments
Post a Comment