The Power of Cloud Computing: Transforming Innovation and Business in the United States
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, cloud computing has emerged as a cornerstone of technological advancement. It offers businesses and individuals unprecedented access to a wide array of tools and resources, enabling them to innovate rapidly and build solutions that were once unimaginable. From infrastructure services like compute, storage, and databases to cutting-edge technologies such as machine learning, data lakes, and analytics, the cloud empowers users to bring their ideas to life with remarkable speed.
One of the most significant advantages of cloud computing is its ability to allow users to scale resources on demand. This means that whether you're a startup looking to test a new concept or an enterprise aiming to expand operations, you can quickly spin up the necessary services without the burden of managing physical hardware. As a result, the time it takes to move from an idea to a working implementation has been drastically reduced, giving organizations the freedom to experiment, iterate, and differentiate their offerings in a competitive market.
Understanding the Different Types of Cloud Computing
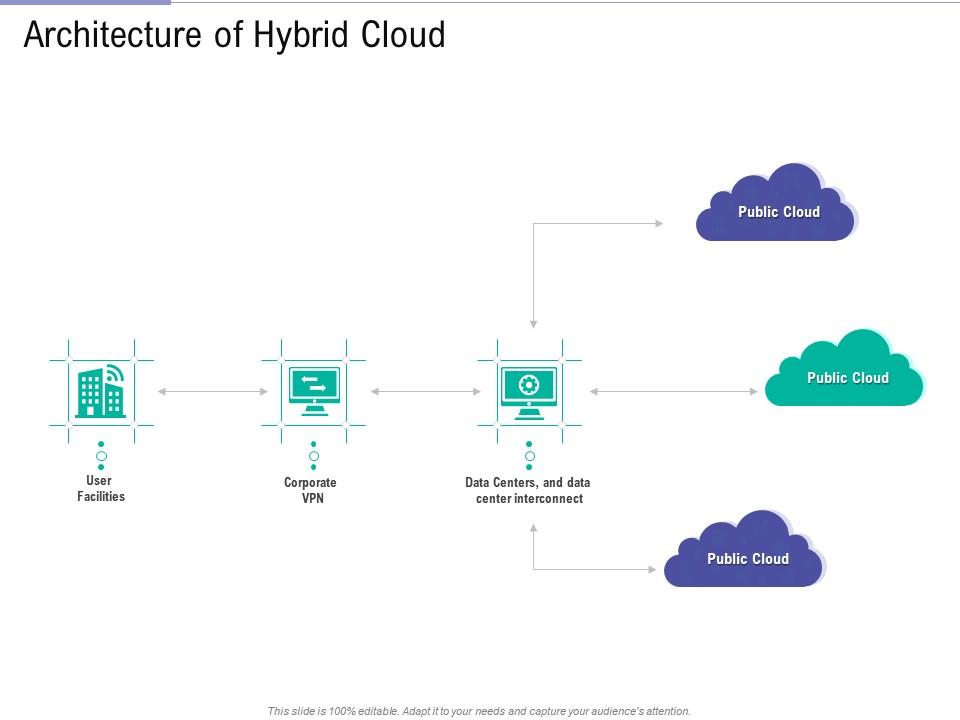
Not all clouds are created equal, and the choice of cloud deployment model can have a major impact on your business strategy. There are three primary types of cloud computing architectures: public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. Each has its own set of benefits and use cases, making it essential for organizations to evaluate which option best aligns with their needs.
-
Public Cloud: In a public cloud model, services and infrastructure are delivered over the internet by third-party providers. This model is ideal for businesses seeking cost-effective scalability and flexibility. Popular examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
-
Private Cloud: A private cloud is dedicated to a single organization, offering enhanced security and control. It is often used by enterprises that handle sensitive data or require customized configurations. Private clouds can be hosted on-premises or by a third party.
-
Hybrid Cloud: This model combines elements of both public and private clouds, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of each. For instance, businesses might use a private cloud for critical data and a public cloud for scalable workloads. Hybrid clouds offer greater flexibility and can be tailored to meet specific business requirements.
How Cloud Computing Works
At its core, cloud computing involves accessing remote servers through the internet to store, manage, and process data. These servers are housed in large data centers and are maintained by cloud service providers. Instead of relying on local servers or personal devices, users can tap into these powerful resources from anywhere, at any time.
This model provides several key benefits, including:
- Flexibility: Users can access computing power and storage as needed, without the constraints of traditional on-premises infrastructure.
- Scalability: Businesses can easily scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring they only pay for what they use.
- Cost Efficiency: By eliminating the need for physical hardware, cloud computing reduces capital expenditures and shifts costs to a more manageable operational model.
The Role of Cloud Computing in Everyday Life
Cloud computing is not just limited to businesses; it plays a vital role in our daily lives. From checking email via Google Gmail to streaming movies on Netflix or playing video games hosted in the cloud, we interact with cloud services on a regular basis. These applications rely on the cloud to deliver seamless experiences, ensuring that users have access to the computing power and storage they need without the hassle of maintaining physical infrastructure.
For example, streaming platforms like Netflix use cloud computing to store vast libraries of content and deliver it to millions of users simultaneously. Similarly, online gaming companies leverage the cloud to host games and provide real-time multiplayer experiences, all while minimizing the need for high-end hardware on the user's end.
Cloud Computing in Business Settings
In the business world, cloud computing has become indispensable, particularly for startups and global enterprises alike. It enables companies to operate more efficiently, reduce costs, and stay agile in a rapidly evolving market. Some of the key business applications of cloud computing include:
- Remote Work: Cloud services make it possible for employees to access data and applications from anywhere, supporting flexible work arrangements and improving productivity.
- Omnichannel Customer Engagement: Businesses can create a seamless customer experience across multiple channels by leveraging cloud-based tools that integrate sales, marketing, and support functions.
- Cutting-Edge Technologies: The cloud provides the infrastructure needed to harness advanced technologies like generative AI and quantum computing, allowing businesses to stay ahead of the curve.
As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, the role of cloud computing will only grow. With its ability to drive innovation, enhance scalability, and support modern work environments, the cloud is shaping the future of technology in the United States and beyond.
Comments
Post a Comment