Blockchain Technology: A Catalyst for Transparent and Sustainable Digital Commons
In the 21st century, the digital landscape is evolving at an unprecedented pace, driven by innovations that challenge traditional systems of governance, ownership, and access. Central to this transformation is the concept of digital commons—shared digital resources such as open-source software, public data repositories, and collaborative knowledge platforms. These commons are essential for fostering innovation, ensuring equitable access to information, and addressing global challenges. However, their sustainability and effectiveness depend on robust governance models. Enter blockchain technology, a decentralized and transparent system that has the potential to revolutionize how we manage and interact with these shared digital resources.
The Role of Blockchain in Enhancing Digital Commons
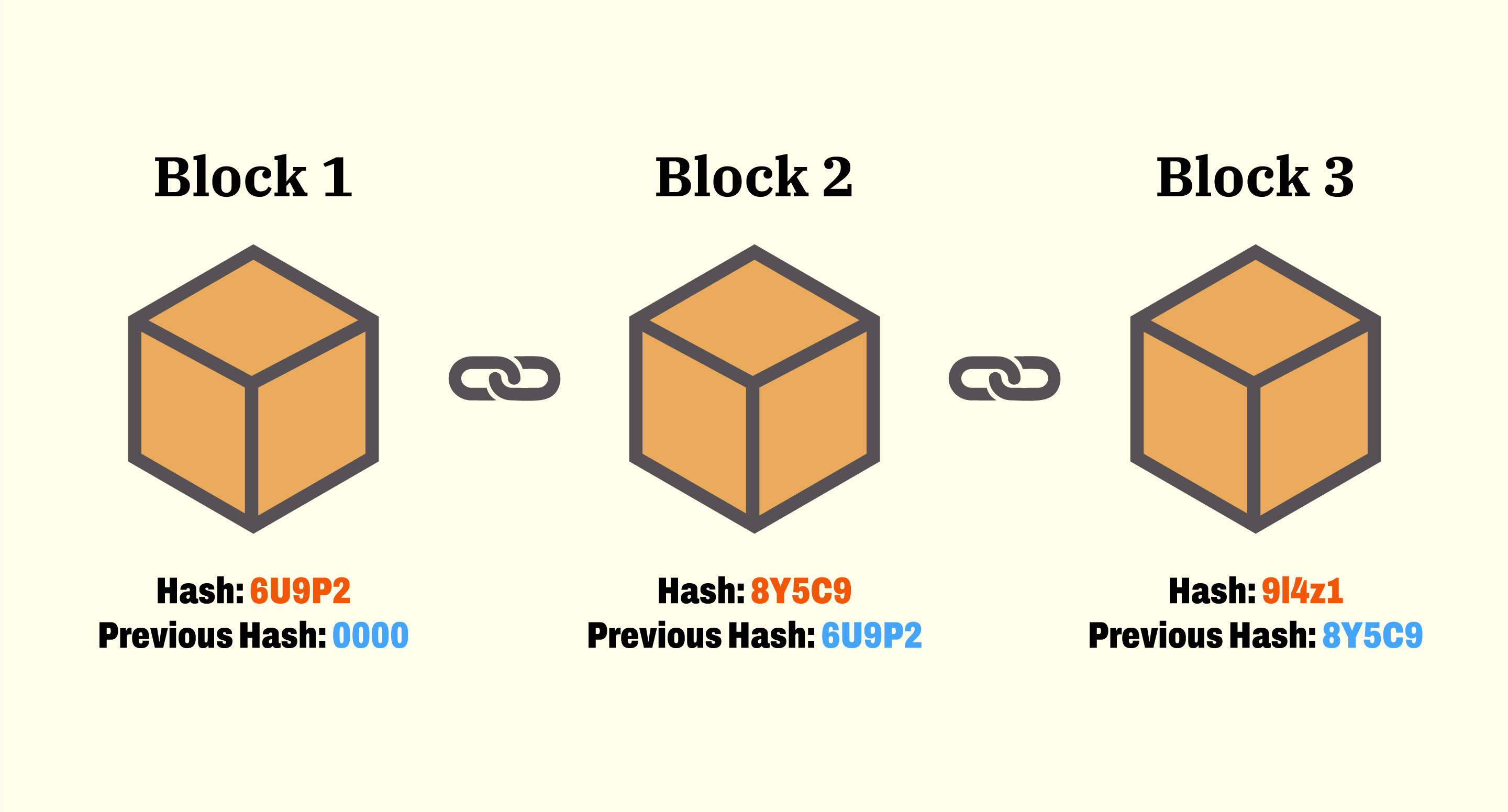
Blockchain technology introduces a new dimension to the governance of digital commons by offering transparent record-keeping, secure decision-making, and immutable verification. Unlike traditional centralized systems, which often struggle with issues like trust, accountability, and scalability, blockchain enables a decentralized framework where all participants can verify transactions and contributions. This not only enhances transparency but also ensures that contributions are fairly recognized and rewarded.
For instance, platforms like GitCoin use blockchain to create decentralized funding models for open-source development, allowing contributors to be compensated for their work. Similarly, blockchain-based voting systems can enhance community governance in digital commons, enabling more democratic and transparent decision-making processes. By leveraging smart contracts, these systems can automate resource allocation, streamline management, and reduce the risk of fraud or manipulation.
Addressing Challenges in Digital Commons
Despite their potential, digital commons face significant challenges that hinder their sustainability and impact. One of the primary issues is securing long-term funding. Unlike commercial ventures, many commons projects lack clear revenue streams, making it difficult to maintain and develop resources. Blockchain-based solutions, such as non-fungible tokens (NFTs), can provide sustainable funding sources while preserving open access. For example, NFTs can be used to monetize digital assets without compromising the principles of openness and collaboration.
Another challenge is maintaining standards and accuracy in open systems. Without traditional gatekeepers, ensuring the reliability of information can be challenging. Blockchain’s consensus mechanisms and reputation systems offer decentralized ways to verify and validate contributions, helping to maintain the integrity of digital commons. Additionally, blockchain-based licensing and rights management systems can simplify the process of tracking and enforcing open licenses across borders, addressing legal complexities associated with intellectual property.
The Need for a Multistakeholder Approach
Realizing the full potential of blockchain-governed digital commons requires a multistakeholder approach involving governments, private sector entities, and civil society. Governments should implement policies that encourage the creation and use of blockchain-based solutions, such as supporting research into decentralized governance models and creating legal frameworks that recognize blockchain-based decision-making processes.
Exploring innovative funding mechanisms is also crucial. Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) and blockchain-based crowdfunding platforms can provide transparent and accountable funding for commons initiatives. Promoting digital literacy and blockchain education is equally important. Initiatives like Blockchain Commons, which offers online courses in blockchain and the digital commons, play a vital role in equipping individuals with the skills needed to participate in and contribute to these ecosystems.
Investing in robust technological infrastructure will further support the creation and maintenance of these new forms of digital commons. By embracing blockchain technology, communities can develop more sustainable and resilient models for sharing and managing digital resources, ultimately fostering greater innovation and collaboration.
Blockchain in Food Supply Chains: A Case Study
Beyond digital commons, blockchain technology is also transforming other critical sectors, such as food supply chains. The integration of blockchain in food supply chains offers transparency, traceability, and security, addressing longstanding challenges in the industry. One notable example is Silal Fresh, a fresh produce division of Silal, which faced difficulties in tracing its products due to gaps in supply chain visibility.
By adopting a blockchain-based solution, Silal Fresh was able to improve traceability, communication, and security across its supply chain. Every touchpoint of a product is recorded in an immutable ledger, providing real-time updates and ensuring that consumers can track the journey of their food from source to shelf. This not only enhances consumer trust and brand loyalty but also improves food safety and quality assurance.
The benefits of blockchain in food supply chains extend beyond individual companies. Improved traceability can lead to faster food recalls, reduced waste, and better compliance with environmental and social standards. As the global population continues to grow, the need for efficient and sustainable food systems becomes increasingly urgent. Blockchain technology offers a promising solution to these challenges, ensuring that food reaches those who need it most.
The Future of Tokenization in Financial Markets
In addition to digital commons and food supply chains, blockchain is also reshaping financial markets through the tokenization of financial assets. Tokenization involves creating a digital representation of physical or financial assets on the blockchain, enabling secure and real-time exchanges. This process is gaining momentum at both institutional and governmental levels, with major players like the Bank of England, Euroclear, and the World Bank exploring tokenized assets.
The benefits of tokenization include reduced operational costs, improved efficiencies, and enhanced liquidity. By streamlining manual processes and automating transactions, blockchain can significantly lower settlement risks and improve market efficiency. For example, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority’s Project Evergreen has demonstrated the first green bond issuance using tokenization, highlighting the potential for sustainable finance.
As more institutions adopt tokenization, the capital markets infrastructure is being brought into the 21st century. This shift not only increases financial inclusion but also opens new opportunities for investors to access a wide range of assets in real time. With the right governance structures in place, tokenization has the potential to redefine the way we trade and manage financial assets globally.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is more than just a tool for innovation—it is a transformative force that can reshape how we govern digital resources, manage supply chains, and conduct financial transactions. By enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency, blockchain offers a powerful solution to some of the most pressing challenges of our time. As we continue to navigate the complexities of the digital age, the integration of blockchain into various sectors will play a crucial role in building a more equitable, sustainable, and interconnected world.
Comments
Post a Comment